Of all factors, government cybersecurity preparedness plays a greater role in saving a country’s critical national infrastructure. However, nothing much seems to change when it comes to government and cybersecurity.
The recent audit of the government cybersecurity preparedness at the state of Utah highlighted a series of ongoing deficiencies in protecting sensitive data and establishing robust cyber defenses within the US state.
Interestingly, similar issues were highlighted in another state audit conducted in Mississippi in 2019.
This interim period of about four years saw an overhaul in global cybersecurity perspectives, preparedness, and the nature of threats. However, a closer look at both audits makes one ask: what’s wrong with government cybersecurity preparedness?
The findings, spanning a period of nearly four years, reveal concerning shortcomings in two distinct US states, Mississippi, and Utah.
Despite the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks and the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures, these government entities have fallen short in safeguarding residents’ personal data and establishing comprehensive security frameworks.
It is not a question of budgets or technology, but policy. The government cybersecurity preparedness in the US needs to shed its pre-pandemic methods and policies.
Why does government cybersecurity preparedness fall short?
Starting in October 2019, the first-ever statewide survey in Mississippi on the government cybersecurity preparedness revealed unsettling results, exposing significant gaps in the state’s cybersecurity policies.
The survey exposed alarming lapses in the protection of personal data, a lack of written procedures to respond to cyberattacks, and numerous state agencies neglecting the legally mandated review process altogether.
These revelations showcased a troubling disregard for cybersecurity best practices and a failure to adequately address the growing threat landscape.
Fast forward to May 2023, where the situation on government cybersecurity preparedness remains dishearteningly similar.
A report published by the state legislature’s watchdog office in Utah has highlighted widespread deficiencies in cybersecurity planning and training across multiple branches of government.
The comprehensive audit on government cybersecurity preparedness conducted by the Office of the Legislative Auditor General’s performance audit of public-sector privacy practices revealed that numerous agencies had failed to implement essential cybersecurity frameworks, neglecting industry-standard controls recommended by organizations such as the Center for Internet Security.
Furthermore, routine cyber hygiene training for employees was not consistently mandated, perpetuating vulnerabilities and leaving government systems exposed to potential breaches.
These revelations are particularly alarming given the multitude of events, including the unprecedented rise in cybersecurity incidents associated with the ongoing pandemic, that have occurred between 2019 and 2023.
Despite the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and the potential consequences of data breaches, the latest audit serves as a stark reminder of the lack of progress made by government entities in fortifying their cyber defenses.
Government cybersecurity: Changing times, unchanged ways
The Office of State Auditor Shad White conducted a cybersecurity audit in 2019 revealing alarming deficiencies in cybersecurity practices within Mississippi government institutions.
The examination f the government cybersecurity preparedness in the state aimed at verifying compliance with the Mississippi Enterprise Security Program and industry-standard cybersecurity protocols, highlighted a concerning lack of adherence to essential security measures.
Fissures started popping up right from the participation of government agencies.

“As required by state law, the Auditor’s office sent a cyber security survey to 125 state agencies, boards, commissions, and universities,” observed Mississippi State Auditor Shad White.
“Only 71 state entities responded to the survey, and several respondents did not complete it. This leaves the status of cyber security in more than 50 state entities completely unknown,”
A situation where state-funded institutions choosing not to respond to the audit should have raised serious concerns about their commitment to cybersecurity and their duty to protect the interests of the State and its citizens.
Among the key requirements highlighted in the analysis is the importance of documenting policies and procedures.
Such documentation serves as a vital framework for establishing effective cybersecurity practices, including infrastructure documentation, risk mitigation procedures, incident reporting and response protocols, and general rules for end-user behavior.
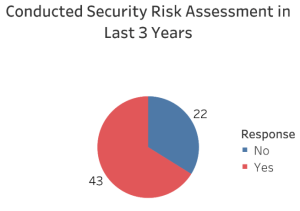
Astonishingly, out of the 71 agencies that did respond to the survey, 11 reported a complete absence of security policy plans or disaster recovery plans. This failure to implement foundational cybersecurity measures leaves these agencies ill-equipped to tackle potential threats and places sensitive information at risk.
One alarming finding is that 22 agencies have not had a third-party Security Risk Assessment conducted, leaving them vulnerable to hacking and non-compliant with state law.
Encryption is crucial for protecting this sensitive data, as it prevents unauthorized access even in the event of a security breach. However, the survey indicates that 38% of agencies reported not encrypting sensitive information, putting the data at high risk.
“The State of Mississippi creates, stores, and maintains a wealth of sensitive information. Health data, tax data, student data, and any number of personally identifiable data are examples of sensitive information,” noted the report.
“It is critical that sensitive information is encrypted when stored or transmitted.”
The survey consisted of 59 questions related to the Enterprise Security Program requirements. The findings presented here highlight only a fraction of the identified problems, serving as examples of the cybersecurity issues within state government.
“In short, the survey found over half of all respondents are less than 75% compliant with state cyber security laws,” said the government auditor’s note.
The audit brought out the failure of numerous state agencies, boards, commissions, and universities to meet these requirements, while the reluctance of several bodies in participating in the audit process revealed concerning systemic apathy.
Government cybersecurity preparedness: Different state, same problems
Flash forward to 2023, this time Utah.
The Office of the Legislative Auditor General, Utah, conducted a performance audit on public-sector privacy practices encompassing the state legislature, judicial branch, local governments, and the education sector.
The deficiencies in establishing cybersecurity frameworks and ensuring routine cyber hygiene training for employees was widespread.
Among the key findings of the report is the breakdown of communication between IT staff and administration regarding the associated risks of cybersecurity.
The lack of effective communication has resulted in costly cyber incidents, with entities that experienced attacks reportedly paying hundreds of thousands to over a million dollars as a consequence.
However, the report also notes a low response rate to the audit, raising concerns about the overall risk to the state.
Harking back to the Mississippi situation, only 37% of over 600 entities returned the survey, potentially indicating a lack of secure cybersecurity networks as a reason for the low response rate.
At the local government level, the audit revealed varying levels of adoption of cybersecurity frameworks. Of the 223 respondents, 57 percent stated that they have adopted a cybersecurity framework.
While 75% of school districts and 56% of county governments reported having adopted a cyber framework, only 39% of towns and cities indicated the same.
“With a response rate of only 37 percent, we are concerned that we were unable to determine the totality of cybersecurity risk to the state,” said the audit report.
“We are concerned about the entities that did not respond to our survey. They may not have adopted a cybersecurity framework and may not have implemented proper controls to decrease cybersecurity attacks,” said the report.
Most alarming was the scale of shortcomings traced to the state level administration.
The Utah Legislature lacked a strategic cybersecurity plan based on industry standards and does not have an incident response planning document.
The legislative IT office, which recently established a cybersecurity division, previously relied on the executive branch’s Division of Technology Services for cyber support.
The Utah judiciary also faced challenges, as it lacks a current strategic plan, with the last cyber plan being published in 2014. The audit also identifies a decline in the number of employees completing the required annual cyber hygiene training within the state court system.
“Many entities can decrease the likelihood of serious cyberattacks through a few simple and effective methods. These include adopting a cybersecurity framework, improving communication between IT leadership and administrative leadership, and requiring employees to complete annual cybersecurity training,” said the Utah audit report.
“Despite the entities’ best efforts to prevent cyberattacks, they can still occur. Therefore, several entities need to adopt an incident response plan to minimize the cost of a potential successful attack,” it added.
However, the common troubles of non-compliance, lack of preparedness, and administrative apathy seems to be running in almost any organization associated with the government.
Faulty cybersecurity preparedness: Beyond state administrations
Government agencies at both the federal and state levels were found falling short in their cybersecurity measures, leaving sensitive data and critical infrastructure vulnerable to attacks.
A yearly audit of NASA’s information security capabilities and practices revealed an overall rating of “Not Effective.”
The audit, conducted by the NASA Office of Inspector General, assessed the agency’s infosec maturity across nine capabilities and found that NASA did not reach the benchmark level of effective infosec program for any of them.
“In order for NASA to reach a higher maturity level, additional controls and processes need to be designed and implemented,” the report said.
Issues identified include a lack of tools and data to understand the state of IT infrastructure, inadequate processes to frame and respond to risks, incomplete network device identification, outdated cybersecurity workforce assessment, and gaps in data protection and privacy standards.
Similarly, the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) released a report highlighting the inadequate response to ransomware threats against public school districts by the Education and Homeland Security departments.
Ransomware attacks against K-12 schools have resulted in significant learning disruptions, with recovery times ranging from two to nine months. Despite the increasing number of incidents, the federal government has not provided sufficient resources to combat the threat.
The Education Department and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) have fallen short in establishing a coordinating council and developing metrics to track the effectiveness of their services to K-12 schools.
The recent audits and reports on cybersecurity practices within government agencies at various levels paint a concerning picture.
Significant shortcomings were revealed in each of these audits, each situation posing risks to sensitive data as well as civic and critical infrastructure.
Government cybersecurity preparedness: Where to patch
The Mississippi audit revealed that numerous state agencies failed to comply with the state’s cybersecurity program, leaving personal data unprotected and lacking written procedures to respond to cyberattacks.
The lack of participation by some agencies in the audit itself is a clear failure of duty, as it hinders the identification and mitigation of potential risks.
It is crucial for government institutions to prioritize cybersecurity and implement robust policies and procedures to safeguard taxpayer funds and sensitive information.
Similarly, the audit in Utah shed light on the insufficient cybersecurity planning and training across multiple branches of government.
Many agencies have not established cybersecurity frameworks or required employees to undergo routine cyber hygiene training, leaving them vulnerable to cyber threats.
The breakdown in communication between IT staff and administration about the associated risks of cybersecurity worsens the already faulty government cybersecurity preparedness, leading to costly incidents and potential breaches.
The audit of NASA’s information security capabilities also indicates a lack of effectiveness in its cybersecurity practices.
The agency’s failure to understand the disposition and state of its IT infrastructure, inadequate data protection and privacy standards, and incomplete network device identification are just a few examples of the vulnerabilities identified.
These weaknesses within NASA’s cybersecurity posture raise concerns about the agency’s ability to protect sensitive information and critical systems.
Taken together, these audits underscore the urgent need for government agencies to prioritize cybersecurity as a fundamental aspect of their operations.
Cyber threats are evolving and becoming increasingly sophisticated, and it is essential for the administration to stay ahead of the curve by improving the government cybersecurity preparedness.
This requires comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks, regular assessments, robust policies and procedures, adequate training for employees, and effective communication between IT staff and administration.
Furthermore, it is crucial for governments to allocate sufficient resources to address cybersecurity risks effectively.
Funding and support should be provided to establish coordinating councils, develop metrics for tracking the effectiveness of cybersecurity services, and enhance overall cyber resilience.
The consequences of neglecting cybersecurity can be severe, ranging from financial losses to compromised data integrity and potential disruptions to critical services.
Governments have a responsibility to protect the interests and well-being of their citizens. Strengthening cybersecurity measures and prioritizing proactive risk management are imperative to maintain public trust, safeguard sensitive information, and ensure the continued functioning of essential government services in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats.