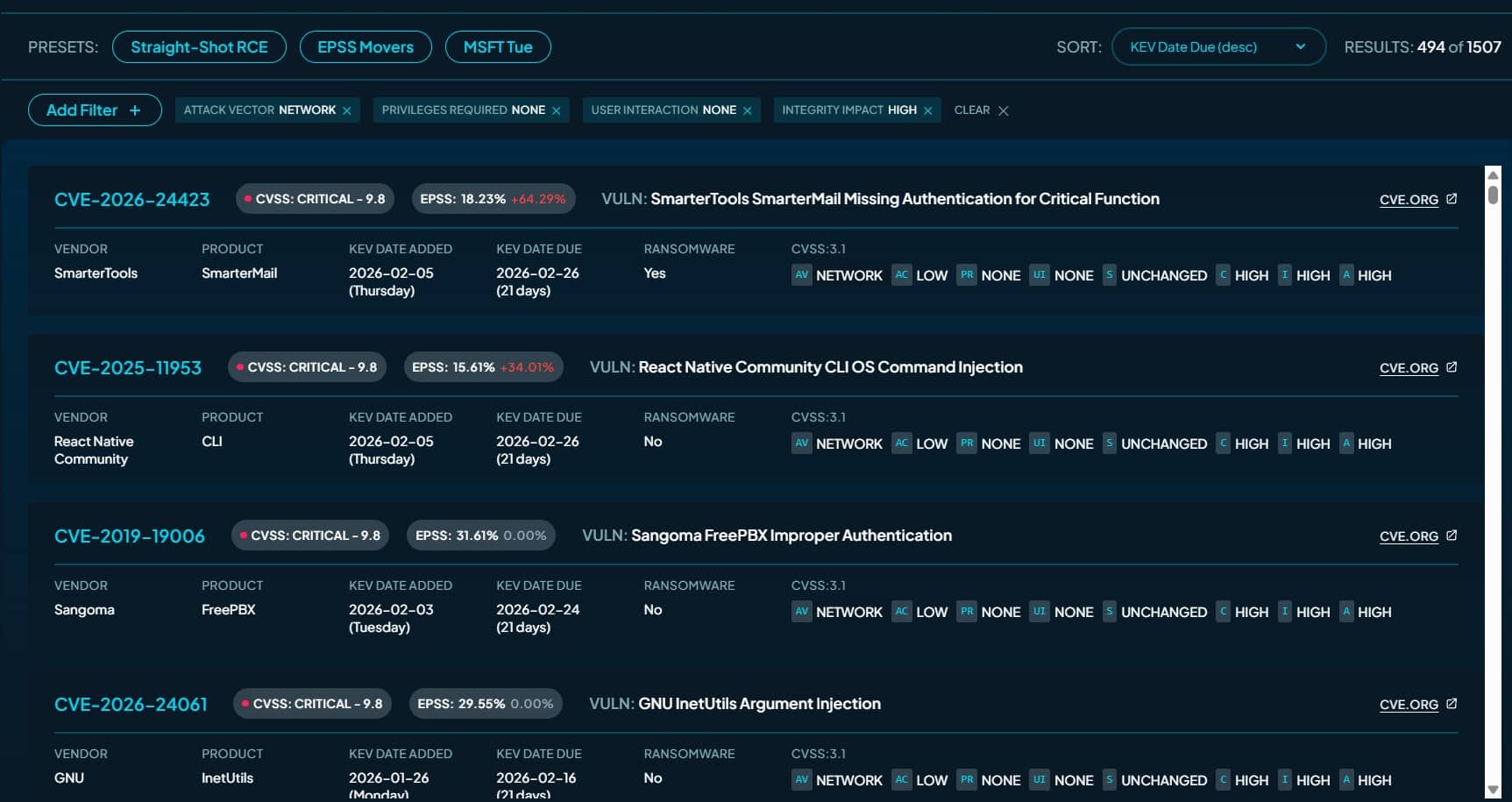
The Snapchat hacking investigation involving an Illinois man accused of stealing and selling private images of hundreds of women is not just another cybercrime case, it is a reminder of how easily social engineering can be weaponized against trust, privacy, and young digital users.
Federal prosecutors say the case exposes a disturbing intersection of identity theft, online exploitation, and misuse of social media platforms that continues to grow largely unchecked.
Kyle Svara, a 26-year-old from Oswego, Illinois, has been charged in federal court in Boston for his role in a wide-scale Snapchat account hacking scheme that targeted nearly 600 women.
According to court documents, Svara used phishing and impersonation tactics to steal Snapchat access codes, gain unauthorized account access, and extract nude or semi-nude images that were later sold or traded online.
Snapchat Hacking Investigation Reveals Scale of Phishing Abuse
At the core of the Snapchat hacking investigation is a textbook example of social engineering. Between May 2020 and February 2021, Svara allegedly gathered emails, phone numbers, and Snapchat usernames using online tools and research techniques. He then deliberately triggered Snapchat’s security system to send one-time access codes to victims.
Using anonymized phone numbers, Svara allegedly impersonated a Snap Inc. representative and texted more than 4,500 women, asking them to share their security codes. About 570 women reportedly complied—handing over access to their accounts without realizing they were being manipulated.
Once inside, prosecutors say Svara accessed at least 59 Snapchat accounts and downloaded private images. These images were allegedly kept, sold, or exchanged on online forums. The investigation found that Svara openly advertised his services on platforms such as Reddit, offering to “get into girls’ snap accounts” for a fee or trade.
Snapchat Hacking for Hire
What makes this Snapchat hacking case especially troubling is that it was not driven solely by curiosity or personal motives. Investigators allege that Svara operated as a hacking-for-hire service. One of his co-conspirators was Steve Waithe, a former Northeastern University track and field coach, who allegedly paid Svara to hack Snapchat accounts of women he coached or knew personally.
Waithe was convicted in November 2023 on multiple counts, including wire fraud and cyberstalking, and sentenced to five years in prison. The link between authority figures and hired cybercriminals adds a deeply unsettling dimension to the case, one that highlights how power dynamics can be exploited through digital tools.
Beyond hired jobs, Svara also allegedly targeted women in and around Plainfield, Illinois, as well as students at Colby College in Maine, suggesting a pattern of opportunistic and localized targeting.
Why the Snapchat Hacking Investigation Matters
This Snapchat hacking investigation features a critical cybersecurity truth: technical defenses mean little when human trust is exploited. The victims did not lose access because Snapchat’s systems failed; they were deceived into handing over the keys themselves.
It also raises serious questions about accountability on social platforms. While Snapchat provides security warnings and access codes, impersonation attacks continue to succeed at scale. The ease with which attackers can pose as platform representatives points to a larger problem of user awareness and platform-level safeguards.
The case echoes other recent investigations, including the indictment of a former University of Michigan football coach accused of hacking thousands of athlete accounts to obtain private images. Together, these cases reveal a troubling pattern—female student athletes being specifically researched, targeted, and exploited.
Legal Consequences
Svara faces charges including aggravated identity theft, wire fraud, computer fraud, conspiracy, and false statements related to child pornography. If convicted, he could face decades in prison, with a cumulative maximum sentence of 32 years. His sentencing is scheduled for May 18.
Federal authorities have urged anyone who believes they may be affected by this Snapchat hacking scheme to come forward.
More than anything, this case serves as a warning. The tools used were not sophisticated exploits or zero-day vulnerabilities—they were lies, impersonation, and manipulation. As this Snapchat hacking investigation shows, the most dangerous cyber threats today often rely on human error, not broken technology.